Terminology
There are multiple panels related to terminology.
- Value Set Panel
- Code System Panel
- Terminology Identifiers Panel
- Terminology Associations Panel
- Concept Maps Panel
- Terminology Browser
It is also possible to initiate a Terminology Report to check the terminologies used in a project. This can be done from the Development Panel.
Terminology Identifiers Panel
The Terminology Identifiers Panel provides an overview of Value Set and Code System versions, sortable by their full identifier.
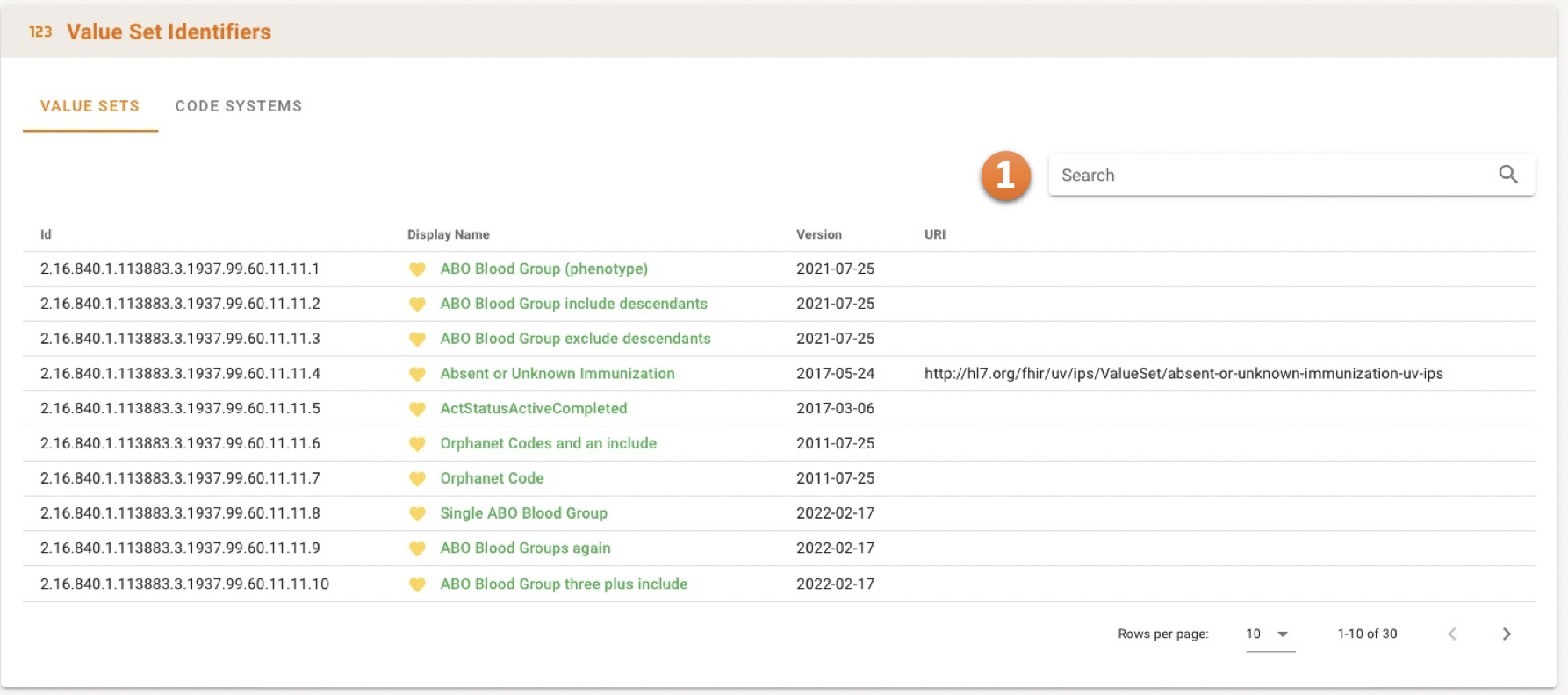
The search bar 1 can be used to filter the artefacts by ID, display name or version label.
Terminology Associations Panel
The Terminology Mappings Panel is used to associate a Concept in a dataset or a Transaction with a Coded Concept or Value Set.
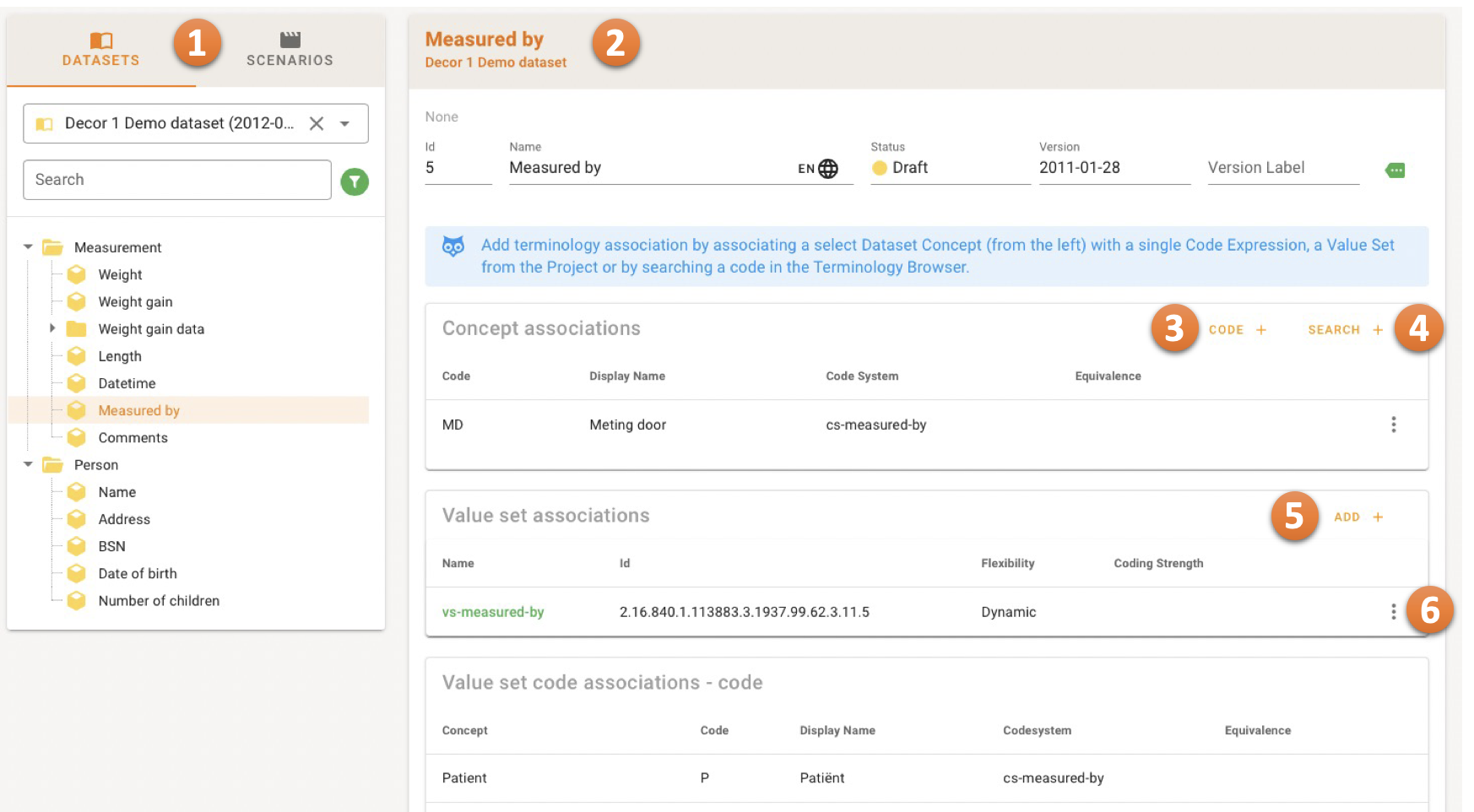
The Navigation Bar on the left 1 offers a Datasets and Scenarios tab.
For managing Dataset Concept Associations, the relevant Dataset should be selected from the dropdown menu. For managing Transaction specific associations, both the Scenario and Transaction have to be selected. Thereafter the concepts are shown in a hierarchical tree.
When a concept is selected, the details are shown in the Detail Card on the right 2.
Associations with a Coded Concept
The CODE button 3 allows adding the association manually.
The SEARCH button 4 navigates to the Terminology Browser. The browser can be used to find a Coded Concept and associate it with the Dataset Concept in scope.
Adding or editing an association supports:
- Equivalence, see: Quality indicator
Associations with a Value Set
The ADD button 5 offers a dialog where a Value Set can be selected.
Adding or editing an association supports:
- Flexibility: Dynamic (always the latest version), or
- Flexibility: Fixed for a specific version.
- Coding Strength, see: Binding strength
Hover the Speed Dial Menu 6 to edit or remove an association.
Associations with codes from a Value Set
Value Set code associations are currently readonly.
Transaction specific associations
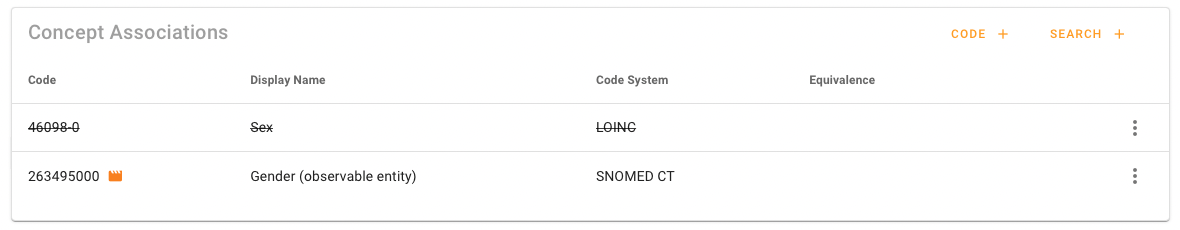
Transaction specific associations are marked with an orange movie icon. The associations that are overwritten are strike-through emphasized. Overwritten associations can be restored. The action is available under the Speed Dial Menu. This will remove all transaction specific associations!
Concept Maps Panel
Concept Maps in ART-DECOR are versionable Objects that are a documentation of the a match-making process of Coded Concepts from two Value Sets. The schematic overview shows two Value Sets and the relationship between a Coded Concept from Value Set A (the source) to B (the target). Mappings are one way relationships, from the source to the target system. While in many cases, the reverse mappings are valid, it is not a rule and cannot be assumed to be the case.
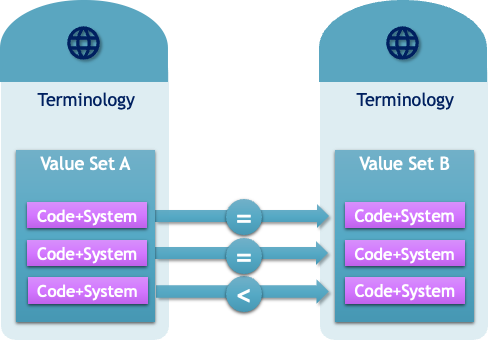
There is also the option (or requirement) to qualify the Relationship. In the example case it might be simple as the codes can be considered top be equivalent, but there are other mappings where relationships that are not only equivalent.
In essence we distinguish between four major types (in FHIR), ART-DECOR essentially follows the ISO Standard ISO/TR 12300:2014 Health informatics, Principles of mapping between terminological systems that knows a few more.

The following table shows the general Relationship Types with definitions and its counterparts in ISO and FHIR. For the ART-DECOR Concept Map Relationship Types are comprised of only those types printed in green bold.
| Relationship (ART‑DECOR) | Definition | ISO Definition | FHIR Definition |
|---|---|---|---|
| equal | The definitions of the concepts are exactly the same (i.e. only grammatical differences) and structural implications of meaning are identical or irrelevant (i.e. intentionally identical) | 1 = Equivalence of meaning; lexical, as well as conceptual. For example, asthma and asthma; ovarian cyst and cyst of ovary. | see equivalent |
| equivalent | The definitions of the concepts mean the same thing (including when structural implications of meaning are considered) (i.e. extensionally identical) | 2 = Equivalence of meaning, but with synonymy. For example, ureteric calculus and ureteric stone; gall stone sand cholelithiasis | equivalent = The definitions of the concepts mean the same thing |
| relatedto | The concepts are related to each other, and have at least some overlap in meaning, but the exact relationship is not known | related-to = The concepts are related to each other, but the exact relationship is not known | |
| wider | Source concept is broader in meaning than the target concept | 3 = Source concept is broader and has a less specific meaning than the target concept/term. For example, obesityand morbid obesity; diabetes anddiabetes mellitus type II. | source-is-broader-than-target= The source concept is broader in meaning than the target concept |
| subsumes | deprecated – The target concept subsumes the meaning of the source concept (e.g. the source is-a target) | ||
| narrower | The source concept is narrower in meaning than the target concept. The sense in which the mapping is narrower SHALL be described in the comments in this case, and applications should be careful when attempting to use these mappings operationally. | 4 = Source concept is narrower and has a more specific meaning than the targetconcept/term. For example, feels ugly andself-image finding; acute renal failuresyndrome secondary to dehydration andacute renal failure syndrome. | source-is-narrower-than-target= The source concept is narrower in meaning than the target concept. |
| specializes | deprecated – The target concept specializes the meaning of the source concept (e.g. the target is-a source) | ||
| inexact | deprecated – The mappings overlap, but both source and target cover additional meaning, or the definitions are imprecise and it is uncertain whether they have the same boundaries to their meaning. The sense in which the mapping is different SHALL be described in the comments in this case, and applications should be careful when attempting to use these mappings operationally. | ||
| unmatched | There is no match for this concept in the destination concept system | 5 = No map is possible. No concept was found in the target with some degree ofequivalence (as measured by any of theother four ratings). | not-related-to = This is an explicit assertion that the target concept is not related to the source concept |
The Concept Map Panel is reachable through the Terminology menu Concept Maps.
The Panel has the usual left part with the list of Concept Maps in the Project and a right part that shows the details once a map has been selected.
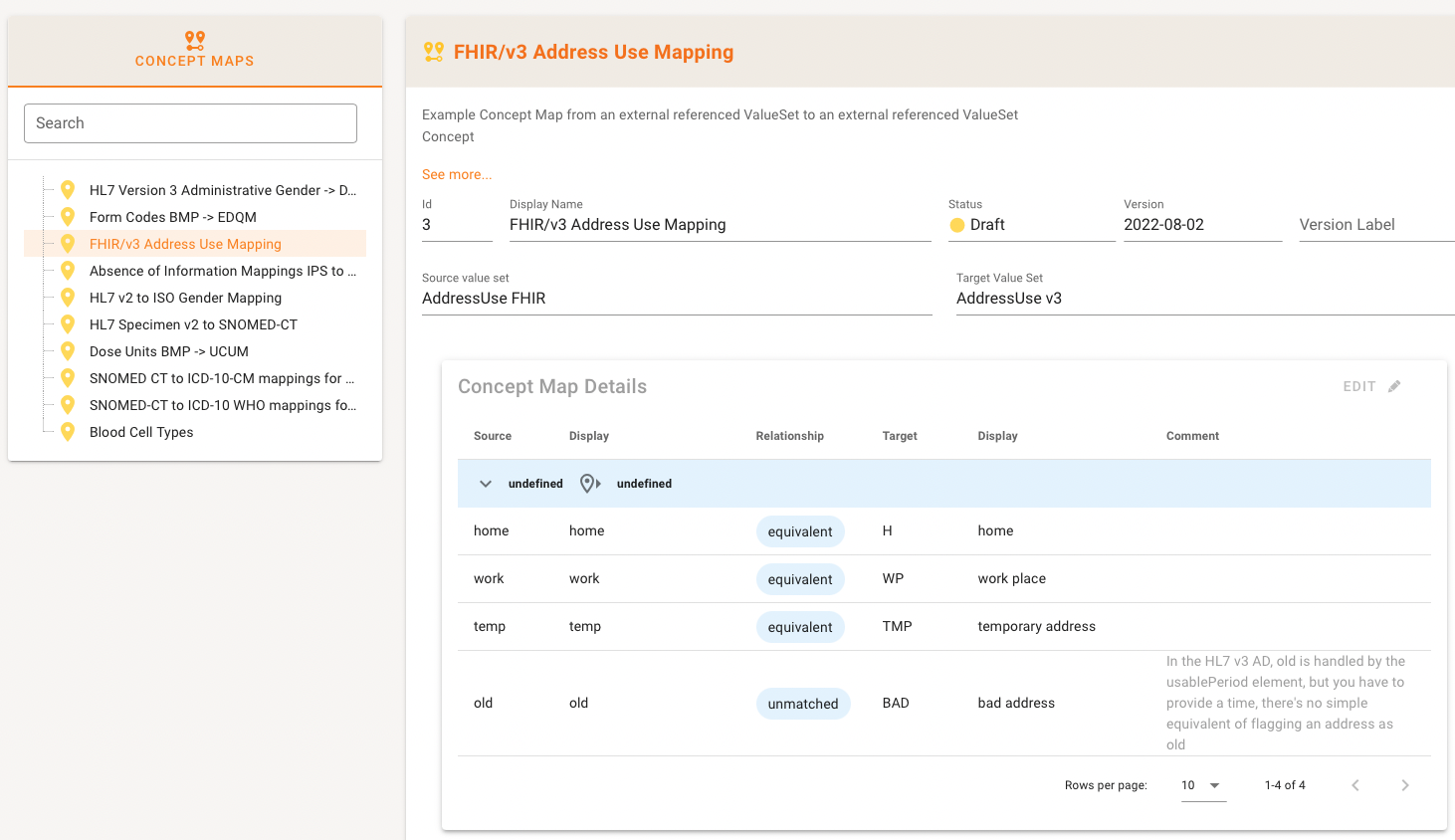
In the detail area you can see the meta data with the speciality here that Source and Target Value Set are shown.
Typically, the Value Sets in the mapping are part of the Project (either as source or in-scope as a reference to a repository). If neither is the case, the detail area indicates that with an error message.

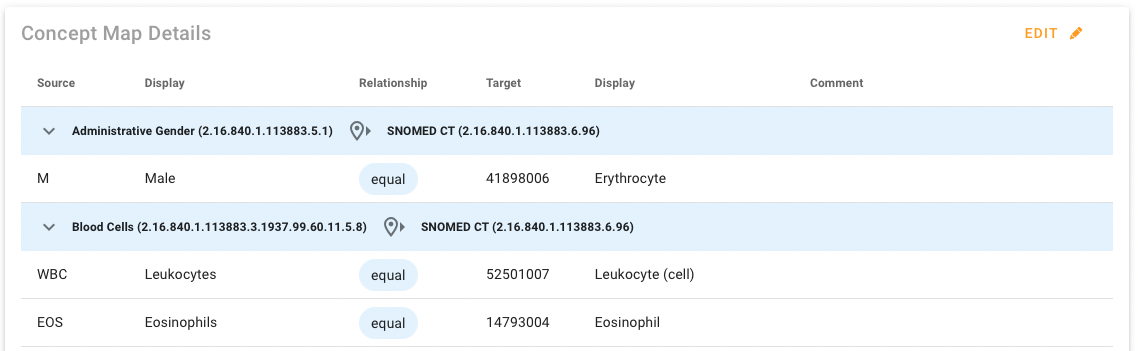
The Concept Map details are grouped by source-target codesystem pairs as expected (heading are the blue rows in the example below). The table shows Source code and display name, Target code and display name and the Relationship Type between the two codes in the middle.
Editing the Concept Map shows the Editor where you can see the Source Value Set with its codes to the left and the Target Value set with codes to the right. In the middle all Maps are shown.
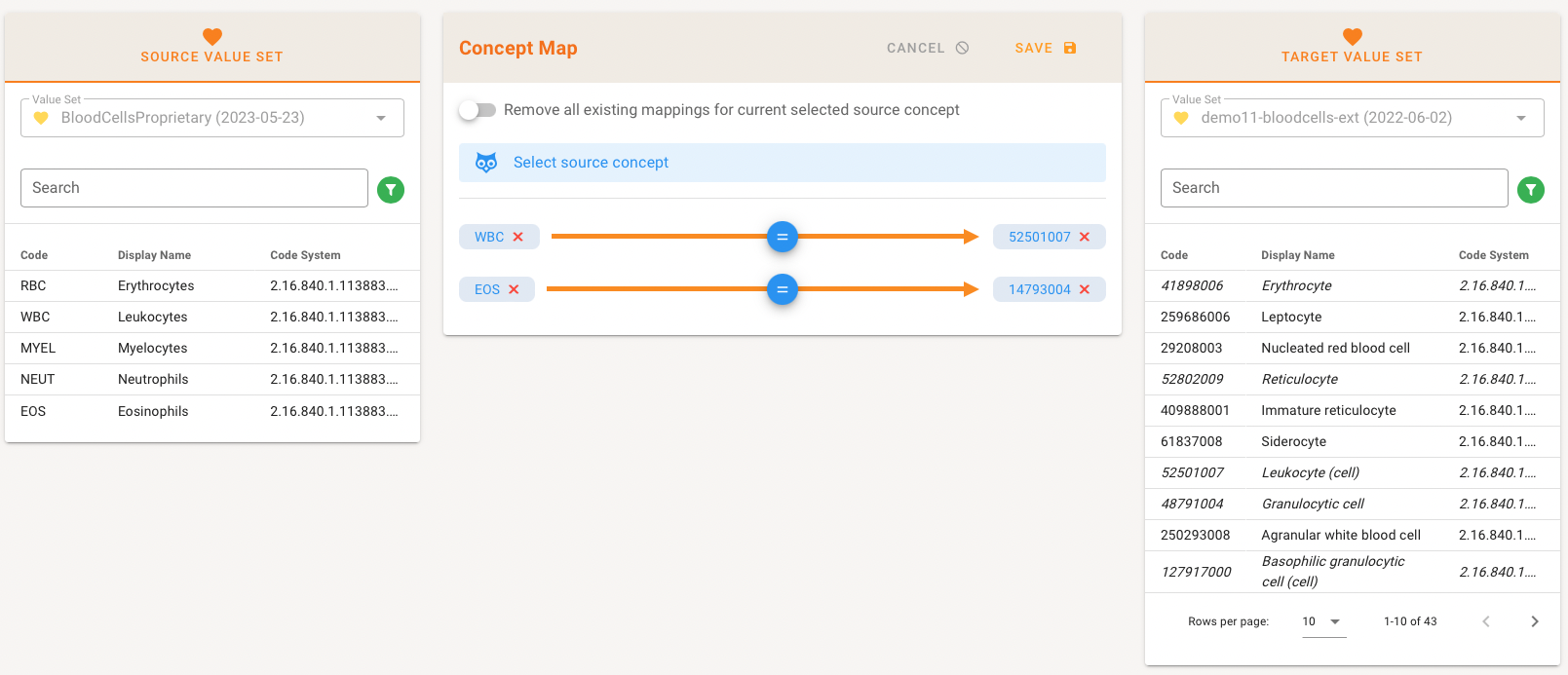
Selecting a Source code automatically shows either the corresponding exsting mapping and advices what the mapping person can do.
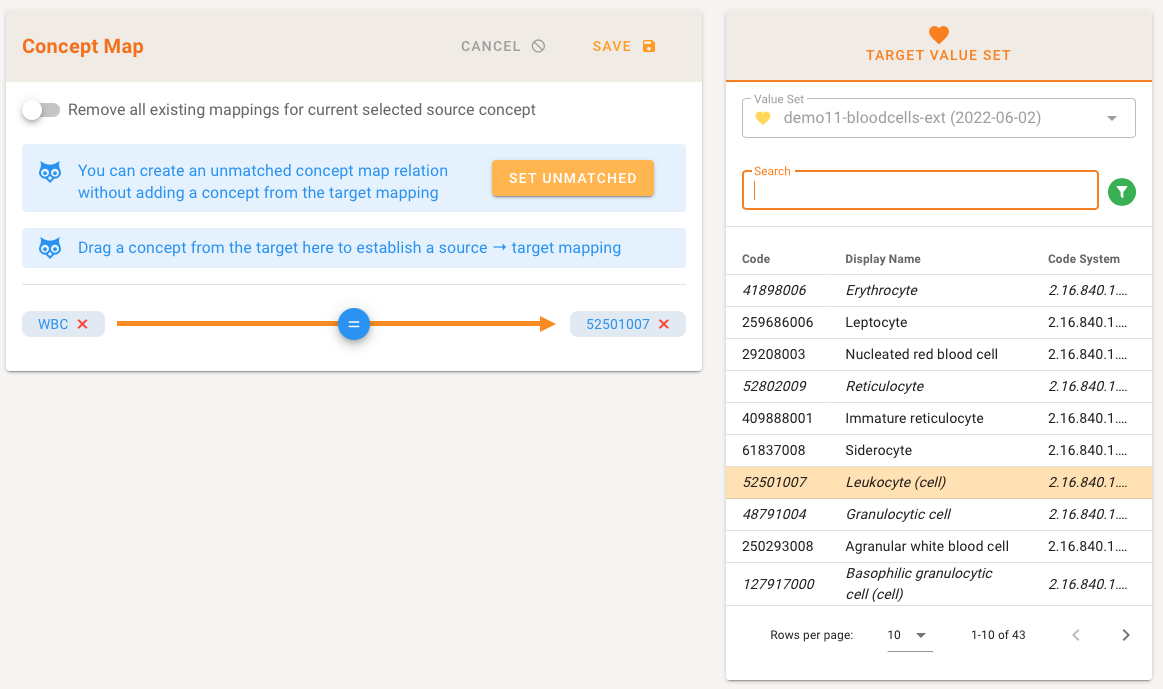
If a mapping exists, the corresponding code is highlighted in the Target value set. You can create an unmatched concept map relation without adding a concept from the target mapping by clicking on "Set Unmatched". Select a code from the Target and drag the concept from the there to establish a Source → Target mapping.
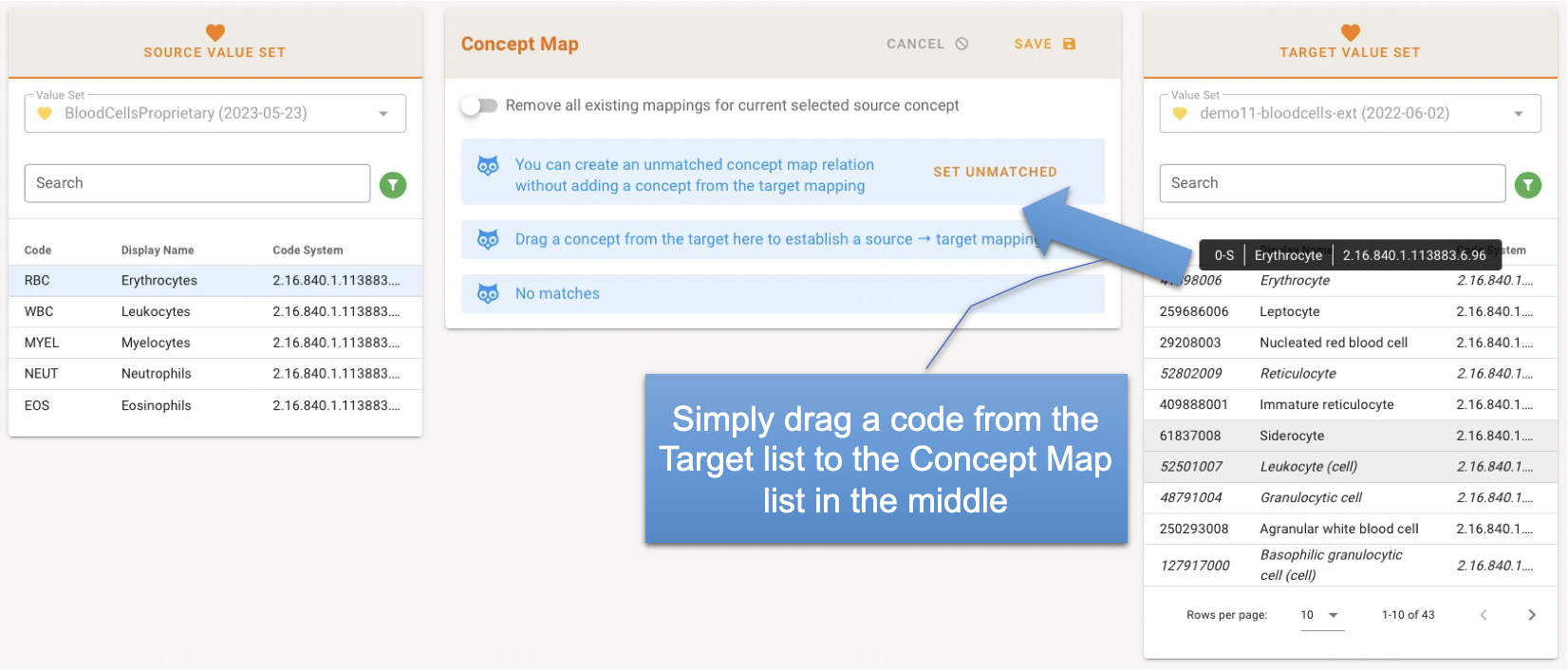
To qualify the Relationship Type a small dialog offers you the type choices (see above). Click "OK" and the concept mapping is added to the list. New mappings appear in green, deleted ones in red. The list got tidied-up after save.
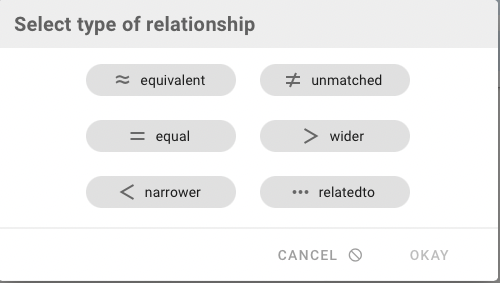
The existing Relationship Type can be changed by clicking in the blue circle. A dialog offers all types, and additionally you can delete the mapping or set it to unmatched. In the upcoming next release you also can add and edit comments for a mapping.
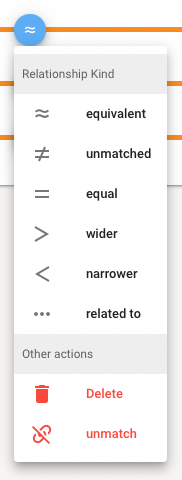
You can unselect an existing map by clicking on the Target Pill in the concept mapping list, or delete an existing mapping by clicking on the Source Pill in the concept mapping list. The latter can also be done by the Relationship Type Dialog (see above).

To get a better overview of the existing concept mapping list, you can hide all already assigned mappings, leaving only unmatched codes in Source and Target list.

Terminology Browser
The Terminology Browser is used for browsing Code Systems.

When opening the Terminology Browser, the available Code Systems are listed 1.
The Browser offers a combined search field 2, where you can switch between searching a term or searching a code. The search mode can be changed by clicking on the icon.
The search field now uses debounce/throttle techniques to initiate the search upon user input. An owl is placed right to the search field to inform about search strategies and options.
General Search hints
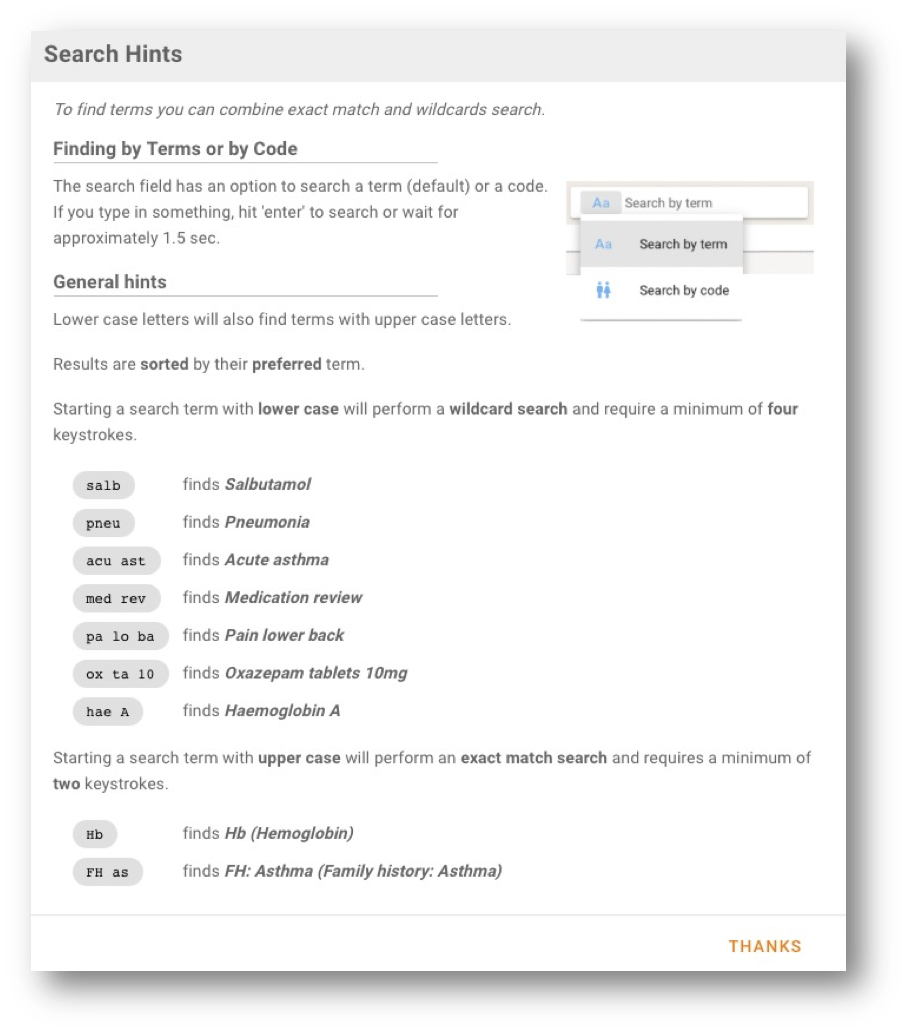
To find terms you can combine exact match and wildcards search. If you type in something, hit 'enter' to search or wait for approximately 1.5 sec to let the search start automatically.
Lower case letters will also find terms with upper case letters.
Results are sorted by the word length of the respective term found.
Starting a search term with lower case will perform a wildcard search and require a minimum of **four **keystrokes.
| Search Term | Finds what? |
|---|---|
salb | finds Salbutamol |
pneu | finds Pneumonia |
acu ast | finds Acute asthma |
med rev | finds Medication review |
pa lo ba | finds Pain lower back |
ox ta 10 | finds Oxazepam tablets 10mg |
hae A | finds Haemoglobin A |
Starting a search term with upper case will perform an exact match search and requires a minimum of two keystrokes.
| Search Term | Finds what? |
|---|---|
Hb | finds Hb (Hemoglobin), note the exact search |
FH as | finds FH: Asthma (Family history: Asthma), note the combination of exact search and wildcard search |
This text is also shown by the owl:
If you are interested in further information on how search and find terms, please have a look at a presentation by Dr Jeremy Rogers, Principal Terminology Specialist at the UK Terminology Centre (NHS Connecting for Health): Browsing SNOMED CT : Finding Terms (PDF), he gave at the IHTSDO I&I SIG in November 2011.
Search results
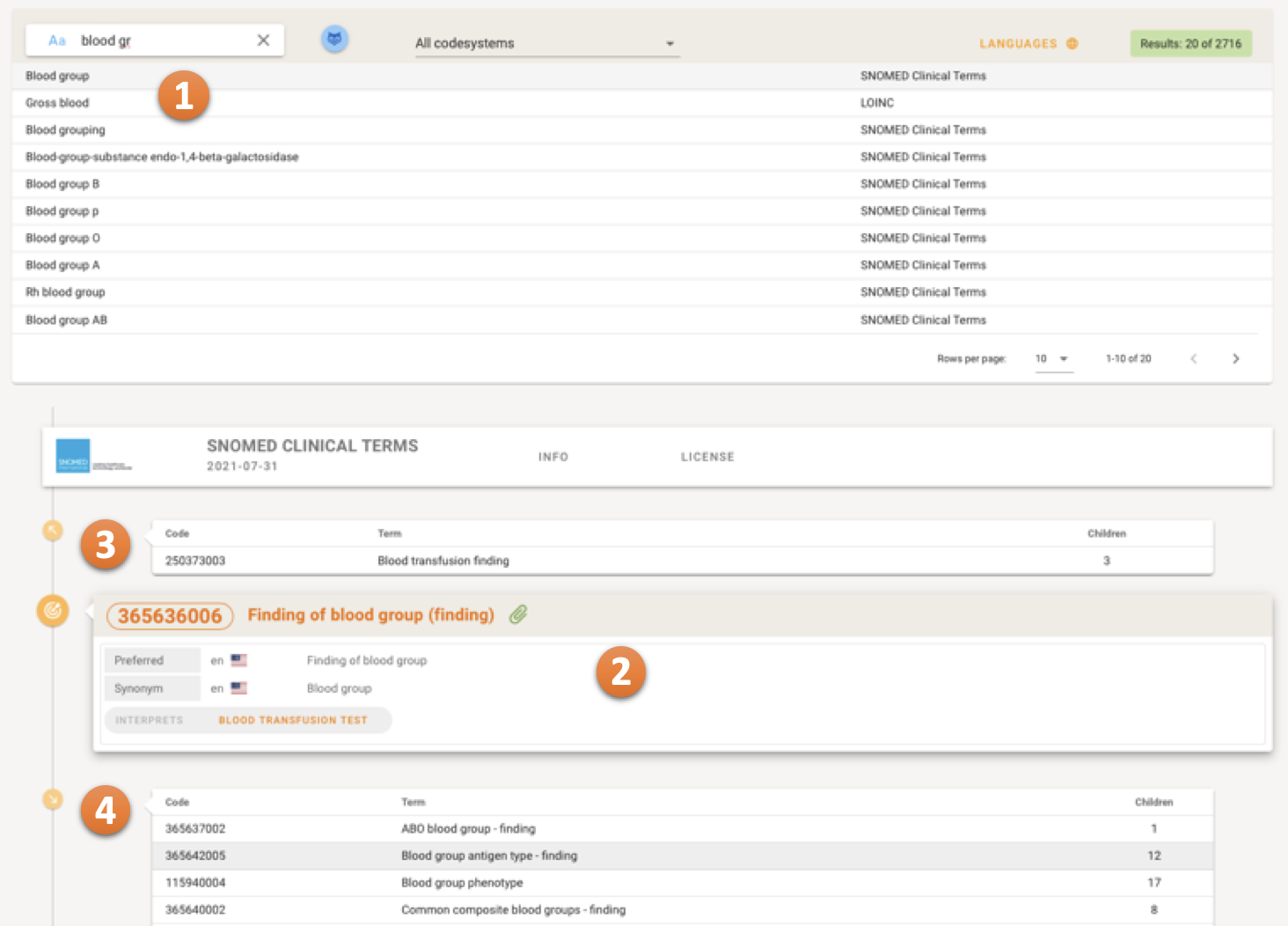
The search results are shown in the top level result table 1, concepts can be selected. The details of the selected Coded Concept are shown in the Concept Detail Part after the result table 2. The Concept Detail Part is able to show the hierarchy or the network of the Coded Concepts. Parents of the selected Coded Concept are listed above the Concept in Focus 3, the children of the selected Coded Concept are listed below 4.
Special SNOMED CT Concept Display
A speciality with the display of SNOMED CT concepts is that Relationsships and Mapping are shown if a concept has ties with other SNOMED concepts or terminologies.
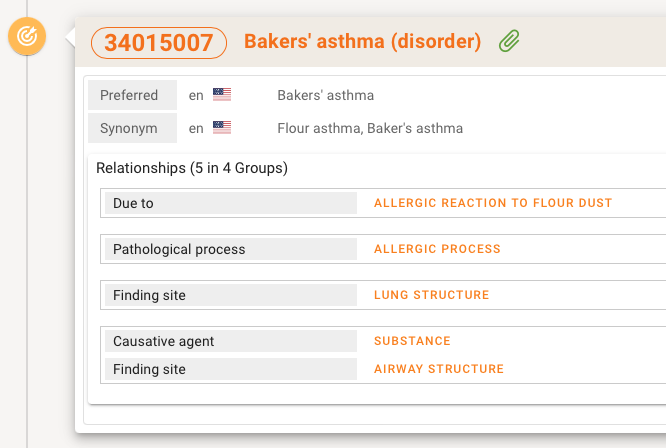
Next to the Fully Specified Name like Baker's asthma (disorder) also the Preferred term synonyms etc are shown in the selected language. Relationships are shown in groups. If there are only a few they are displayed directly in a table, if are more there will be a accordion to open and close to keep the overview cleaner.
Special LOINC search filter
There have been made some Enhancements for Terminology Browser regarding LOINC. A filter option appears when LOINC is selected to be the only Codesystem to be searched in and offers the following dialog:
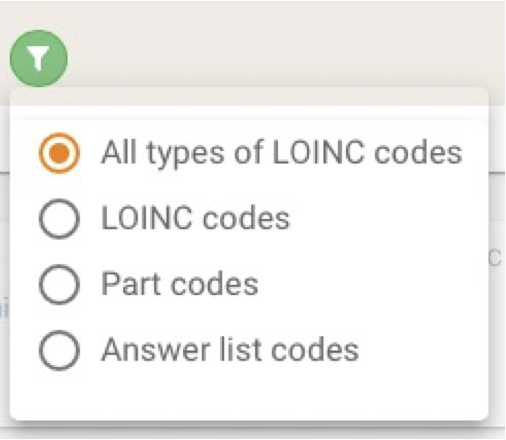
With this one can filter a search on LOINC concepts to display
- all types of LOINC codes,
- original LOINC codes with fully-specified names,
- The LOINC PART codes (LP), the atomic elements that comprise a fully-specified LOINC name, or
- Answer lists codes (LL), and answer string codes(LA).
On LOINC codes and additional content in the LOINC distribution, i. e. LOINC Parts and Part hierarchies (LP) as well as LOINC Answers (LA) and Answer Lists (LL) visit the documentation at loinc.org or an information page about Features of LOINC by SNOMED International
